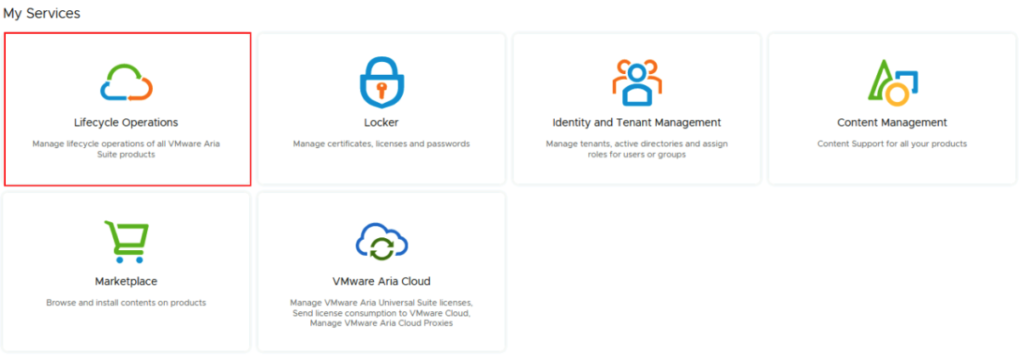
| 5.1.0.0 | bundle-99536 | 640.0MB | ESX_HOST-8.0.2-22380479 | PATCH | efca585c-4fd8-4ec4-9b08-c50701aa2f7d |
| bundle-99541 | 10500.4MB | NSX_T_MANAGER-4.1.2.1.0-22667789 | PATCH | 39759b15-d985-4c15-85d6-7d44fd24df45 |
| bundle-99539 | 2089.2MB | SDDC_MANAGER_VCF-5.1.0.0-22688368 | PATCH | b9308692-c98a-4afc-b49f-601f16105d92 |
| bundle-99540 | 0.0MB | SDDC_MANAGER_VCF-5.1.0.0-22688368 | PATCH(Drift) | f3a11b49-4209-4c2b-8b26-aea98b1f8450 |
| bundle-99537 | 16801.6MB | VCENTER-8.0.2.00100-22617221 | PATCH | 0a1ba239-eab9-41c6-b0e6-9738a463bdbe |
| bundle-99542 | 14606.2MB | NSX_T_MANAGER-4.1.2.1.0-22667789 | INSTALL | c5a39cf5-eca2-4206-8375-082f827612b8 |
| bundle-99538 | 10493.0MB | VCENTER-8.0.2.00100-22617221 | INSTALL | 96cf61e1-85b3-461f-8dfe-5abbeed33ab7 |
| 5.0.0.1 | bundle-94375 | 2044.9MB | SDDC_MANAGER_VCF-5.0.0.1-22485660 | PATCH | 8fe51a93-ff6b-45e1-b9b9-49ad60612703 |
| bundle-94376 | 251.5MB | SDDC_MANAGER_VCF-5.0.0.1-22485660 | PATCH(Drift) | 0602cf8f-9a37-4b38-90ba-f26a19a80cf6 |
| 5.0.0.0 | bundle-80035 | 599.5MB | ESX_HOST-8.0.1-21813344 | PATCH | ef970211-02bf-429a-8edd-91f3bc7c1b42 |
| bundle-80031 | 10089.9MB | NSX_T_MANAGER-4.1.0.2.0-21761691 | PATCH | 3ae76665-4c93-422e-9af8-aafe79a1ee7f |
| bundle-80029 | 2044.7MB | SDDC_MANAGER_VCF-5.0.0.0-21822418 | PATCH | b562189e-0c93-489e-a0b9-e12b01efffb8 |
| bundle-80030 | 251.3MB | SDDC_MANAGER_VCF-5.0.0.0-21822418 | PATCH(Drift) | 393fb05f-23ff-47d1-8b84-db39647677ce |
| bundle-80033 | 9867.6MB | VCENTER-8.0.1.00100-21815093 | PATCH | b862f68d-22a8-457d-a85d-56d72370076e |
| bundle-80032 | 13874.6MB | NSX_T_MANAGER-4.1.0.2.0-21761691 | INSTALL | 7df70351-902f-49e4-a366-553f340d2f3a |
| bundle-80034 | 9867.6MB | VCENTER-8.0.1.00100-21815093 | INSTALL | b1f5bf8e-c133-44a3-9393-efa772c9c0ce |
| 4.5.2.0 | bundle-83610 | 382.1MB | ESX_HOST-7.0.3-21930508 | PATCH | b9462fde-a7d0-4965-b217-cd09bd21bcc5 |
| bundle-87318 | 8615.4MB | NSX_T_MANAGER-3.2.3.1.0-22104592 | PATCH | 259b722b-f8b5-4b4c-9e71-4ebe135cd38e |
| bundle-88445 | 2012.6MB | SDDC_MANAGER_VCF-4.5.2.0-22223457 | PATCH | 363bd141-7d19-4287-9c7a-091c11042ca0 |
| bundle-88446 | 250.5MB | SDDC_MANAGER_VCF-4.5.2.0-22223457 | PATCH(Drift) | 85192dee-1d47-4211-bbdb-999d604f601f |
| bundle-81146 | 6420.0MB | VCENTER-7.0.3.01500-21784236 | PATCH | 4ac2b679-5e5b-43a6-b74b-5fd4e3c978c0 |
| bundle-87319 | 10618.2MB | NSX_T_MANAGER-3.2.3.1.0-22104592 | INSTALL | fcde592c-7a6c-4c92-a6b3-669833dc6910 |
| bundle-81147 | 8575.4MB | VCENTER-7.0.3.01500-21784236 | INSTALL | 659351d3-9d66-45d6-84b0-14451f54cd6f |
| 4.5.1.0 | bundle-73789 | 381.8MB | ESX_HOST-7.0.3-21424296 | PATCH | 2b458531-b783-458e-bc43-3da1ddcd096f |
| bundle-73785 | 8402.7MB | NSX_T_MANAGER-3.2.2.1.0-21487560 | PATCH | e5f9e44f-9123-425e-bee9-07806379d671 |
| bundle-77261 | 2150.0MB | SDDC_MANAGER_VCF-4.5.1.0-21682411 | PATCH | 65b6d750-5ef3-4456-b4c2-65ef96048fb6 |
| bundle-77262 | 250.2MB | SDDC_MANAGER_VCF-4.5.1.0-21682411 | PATCH(Drift) | 8a132cc7-f9b7-4f69-b654-7ea8f7059905 |
| bundle-73787 | 6419.8MB | VCENTER-7.0.3.01400-21477706 | PATCH | 3b8ae94b-582b-4356-b152-2b01e947a072 |
| bundle-73786 | 10461.8MB | NSX_T_MANAGER-3.2.2.1.0-21487560 | INSTALL | f90627d1-a038-4771-9a8a-dfbe1ffa760b |
| bundle-73788 | 8575.1MB | VCENTER-7.0.3.01400-21477706 | INSTALL | 37ec3570-d827-4f32-8eac-92e2b6e21964 |
| 4.5.0.0 | bundle-61598 | 382.9MB | ESX_HOST-7.0.3-20328353 | PATCH | c6a50311-47be-4b53-891d-9f5ecb75d087 |
| bundle-62768 | 8064.0MB | NSX_T_MANAGER-3.2.1.2.0-20541212 | PATCH | 4f2f5d65-53ca-4b58-a85c-49d5b337cc64 |
| bundle-63599 | 2106.0MB | SDDC_MANAGER_VCF-4.5.0.0-20612863 | PATCH | b984c5e4-167a-4886-8f23-be34c9176ca9 |
| bundle-63600 | 247.6MB | SDDC_MANAGER_VCF-4.5.0.0-20612863 | PATCH(Drift) | 4581e5e3-b82f-46b9-99cc-e35584f14de0 |
| bundle-61594 | 6381.1MB | VCENTER-7.0.3.01000-20395099 | PATCH | 34b75350-c552-4c93-b306-75658a3332a4 |
| bundle-62769 | 10053.7MB | NSX_T_MANAGER-3.2.1.2.0-20541212 | INSTALL | 4fe5a96f-d5c3-4730-9970-6d94bc5a63af |
| bundle-61596 | 8344.2MB | VCENTER-7.0.3.01000-20395099 | INSTALL | 8da5d209-c8ac-493f-9e6a-f00a5bd5f155 |
| 4.4.1.1 | bundle-58347 | 10246.1MB | SDDC_MANAGER_VCF-4.4.1.1-19948546 | PATCH | 193486eb-53f5-40c7-8012-b5dcab515ebf |
| bundle-58348 | 233.8MB | SDDC_MANAGER_VCF-4.4.1.1-19948546 | PATCH(Drift) | 3c32c5d6-b5e0-49c6-9a86-90bcd3de671e |
| 4.4.1.0 | bundle-56937 | 395.5MB | ESX_HOST-7.0.3-19482537 | PATCH | 043e2b99-b36f-45b9-a4a2-1632a24764ef |
| bundle-57347 | 7127.2MB | NSX_T_MANAGER-3.1.3.7.4-19762317 | PATCH | 193486eb-53f5-40c7-8012-b5dcab515ebf |
| bundle-57344 | 10246.2MB | SDDC_MANAGER_VCF-4.4.1.0-19766960 | PATCH | 13d87a53-298d-4ee5-98ca-b9e10eece7a5 |
| bundle-57346 | 233.8MB | SDDC_MANAGER_VCF-4.4.1.0-19766960 | PATCH(Drift) | 8c178f33-b28d-47d0-88da-aa94f309a042 |
| bundle-55743 | 7139.0MB | VCENTER-7.0.3.00500-19480866 | PATCH | 05be2afd-990d-45bd-9472-fab032e8c696 |
| bundle-57348 | 8535.7MB | NSX_T_MANAGER-3.1.3.7.4-19762317 | INSTALL | 3c32c5d6-b5e0-49c6-9a86-90bcd3de671e |
| bundle-55745 | 9202.7MB | VCENTER-7.0.3.00500-19480866 | INSTALL | 4073e1c9-4eeb-4d46-97b5-374daa24be41 |
| 4.4.0.0 | bundle-52995 | 395.3MB | ESX_HOST-7.0.3-19193900 | PATCH | d214e445-8509-4d50-adac-59d56acd86ae |
| bundle-52980 | 7154.5MB | NSX_T_MANAGER-3.1.3.5.0-19068434 | PATCH | 348187d2-9930-41d6-9ee1-345857e53a3f |
| bundle-53431 | 10188.6MB | SDDC_MANAGER_VCF-4.4.0.0-19312029 | PATCH | 4f22c22f-441d-4ed9-bb70-697d10bcf028 |
| bundle-53432 | 230.3MB | SDDC_MANAGER_VCF-4.4.0.0-19312029 | PATCH(Drift) | 54485cb4-8db2-4e86-8962-5c4fc54d5727 |
| bundle-56535 | 230.4MB | SDDC_MANAGER_VCF-4.4.0.0-19617653 | PATCH(Drift) | b27c6275-742c-4d51-a907-eba0e158ede3 |
| bundle-52986 | 7223.8MB | VCENTER-7.0.3.00300-19234570 | PATCH | 3bbd1018-1e3f-478d-b201-4287aeb136d8 |
| bundle-52982 | 8610.0MB | NSX_T_MANAGER-3.1.3.5.0-19068434 | INSTALL | 7ae68403-5863-4fcf-8886-f27460c59e85 |
| bundle-52990 | 9244.9MB | VCENTER-7.0.3.00300-19234570 | INSTALL | 7b7816d6-64f9-42a1-be35-3c5d185f08a3 |
| 4.3.1.1 | bundle-52704 | 10695.5MB | SDDC_MANAGER_VCF-4.3.1.1-19235535 | PATCH | 4ea809be-5359-4ac8-b32f-2337c0820d8b |
| bundle-52705 | 230.5MB | SDDC_MANAGER_VCF-4.3.1.1-19235535 | PATCH(Drift) | fd85a861-a972-4da8-b708-8b35aa897e25 |
| 4.3.1.0 | bundle-47505 | 389.4MB | ESX_HOST-7.0.2-18426014 | PATCH | 50f69840-b920-4d1b-81fa-bb934fa13c24 |
| bundle-47501 | 7105.9MB | NSX_T_MANAGER-3.1.3.1.0-18504668 | PATCH | 2f39eed1-94e3-4295-937d-2ea785a2485a |
| bundle-48390 | 10336.5MB | SDDC_MANAGER_VCF-4.3.1.0-18624509 | PATCH | 4162045d-0b25-4ca3-8e38-0371908ed9e6 |
| bundle-48392 | 230.5MB | SDDC_MANAGER_VCF-4.3.1.0-18624509 | PATCH(Drift) | 8f26c34a-7488-4960-aaf7-276ba313846b |
| bundle-47503 | 5394.0MB | VCENTER-7.0.2.00500-18455184 | PATCH | 47d01e0c-ae43-4f74-a57a-b8b3ecbe878b |
| bundle-47502 | 8501.4MB | NSX_T_MANAGER-3.1.3.1.0-18504668 | INSTALL | 9e3175b7-57bc-49cf-8e22-c3885061b48a |
| bundle-47504 | 7383.3MB | VCENTER-7.0.2.00500-18455184 | INSTALL | c49b858d-ed29-48bb-9d13-403d96a3ece3 |
| 4.3.0.0 | bundle-43745 | 390.1MB | ESX_HOST-7.0.2-17867351 | PATCH | 1625a9f9-a96b-4dda-98c6-58938fb29667 |
| bundle-46466 | 7123.1MB | NSX_T_MANAGER-3.1.3.0.0-18328989 | PATCH | 104298b4-bee8-4eae-9791-fc8ff5516f31 |
| bundle-47006 | 10331.2MB | SDDC_MANAGER_VCF-4.3.0.0-18433963 | PATCH | 3f44edc1-6862-4d85-b646-a6bc24698c32 |
| bundle-47008 | 230.3MB | SDDC_MANAGER_VCF-4.3.0.0-18433963 | PATCH(Drift) | 5c1a58d6-2e2d-45bf-960a-5d05b7fee2e3 |
| bundle-46468 | 5394.4MB | VCENTER-7.0.2.00400-18356314 | PATCH | 8d83266a-3b96-467c-8071-74617e10da05 |
| bundle-46467 | 8568.5MB | NSX_T_MANAGER-3.1.3.0.0-18328989 | INSTALL | f14e528f-df76-447d-a235-93b069291f5c |
| bundle-46469 | 7383.7MB | VCENTER-7.0.2.00400-18356314 | INSTALL | 3f560300-18e9-4d9b-bcf5-0b4688c7612b |
| 4.2.1.0 | bundle-42515 | 6995.1MB | NSX_T_MANAGER-3.1.2.0.0-17883596 | PATCH | c6550bcc-9519-423f-b383-625774fed5a6 |
| bundle-42905 | 10142.7MB | SDDC_MANAGER_VCF-4.2.1.0-18016307 | PATCH | df3c4a11-cca4-4cad-b776-35f2035633dd |
| bundle-42906 | 209.3MB | SDDC_MANAGER_VCF-4.2.1.0-18016307 | PATCH(Drift) | a534958a-5af3-4728-bcfc-4196e813f6fe |
| bundle-42521 | 5114.4MB | VCENTER-7.0.1.00301-17956102 | PATCH | 731433e4-122e-40a9-aaba-3ebc1be133d3 |
| bundle-42519 | 8394.9MB | NSX_T_MANAGER-3.1.2.0.0-17883596 | INSTALL | 5881bb39-180f-4563-b434-824d9aa10413 |
| bundle-42522 | 7722.8MB | VCENTER-7.0.1.00301-17956102 | INSTALL | 300a8dcd-c774-4c22-9ea0-b0f08d38e004 |
| 4.2.0.0 | bundle-37983 | 369.0MB | ESX_HOST-7.0.1-17551050 | PATCH | e7ee206d-069f-4982-8271-38e7970dcf9a |
| bundle-32810 | 7057.7MB | NSX_T_MANAGER-3.1.0.0.0-17107167 | PATCH | ff249395-d58a-4d3d-8111-9237fe6a6a45 |
| bundle-37979 | 10070.0MB | SDDC_MANAGER_VCF-4.2.0.0-17559673 | PATCH | 906c8d8f-c28d-4122-8720-43be7af2cbfd |
| bundle-37982 | 209.3MB | SDDC_MANAGER_VCF-4.2.0.0-17559673 | PATCH(Drift) | e53edad7-26df-4282-8874-d1724e63ac5b |
| bundle-35321 | 5140.8MB | VCENTER-7.0.1.00200-17327517 | PATCH | a9938c7e-d30c-4ce9-adab-831f835e6c12 |
| bundle-32811 | 8427.7MB | NSX_T_MANAGER-3.1.0.0.0-17107167 | INSTALL | 1cce3a86-7292-4c91-b0db-20274f2c741d |
| bundle-35322 | 7749.3MB | VCENTER-7.0.1.00200-17327517 | INSTALL | 9d272a97-9a55-492e-b661-0a8f3f2dfd4a |