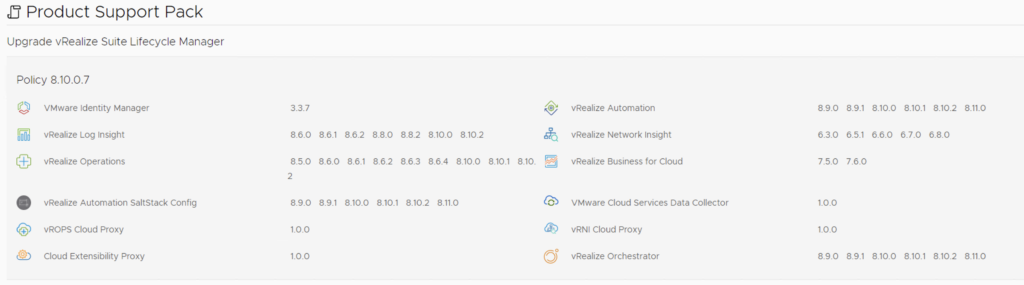
In this post i will go over upgrading my 8.x SSC appliance to 8.11.1. As a pre requirement we do need to have vRSLCM (vRealize Lifecycle Manager) upgraded to 8.11.1. Instructions can be found here. The upgrade does not include the latest PSPACK that contains the 8.11.1 SaltStack Config release. Instructions to get the PSPACK can be found on my other blog post here.
To get started we can go to vRealize Lifecycle Manager -> Lifecycle Operations -> Settings -> Binary Mapping. (If you haven’t added your My VMware credentials you will need to do that first by going to vRealize Lifecycle Manager -> Lifecycle Operations -> Settings -> My VMware)

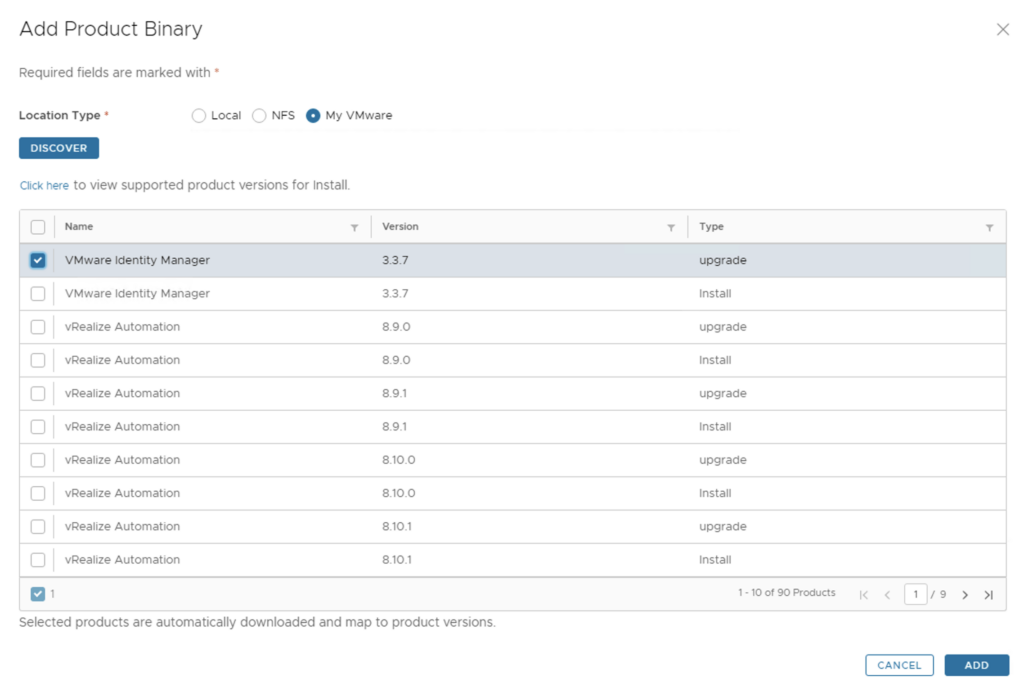
Click on Add Binaries under Product Binaries

Select My VMware and click on Discover

We can see a list of binaries that have been discovered. We can select what we need and click on Add
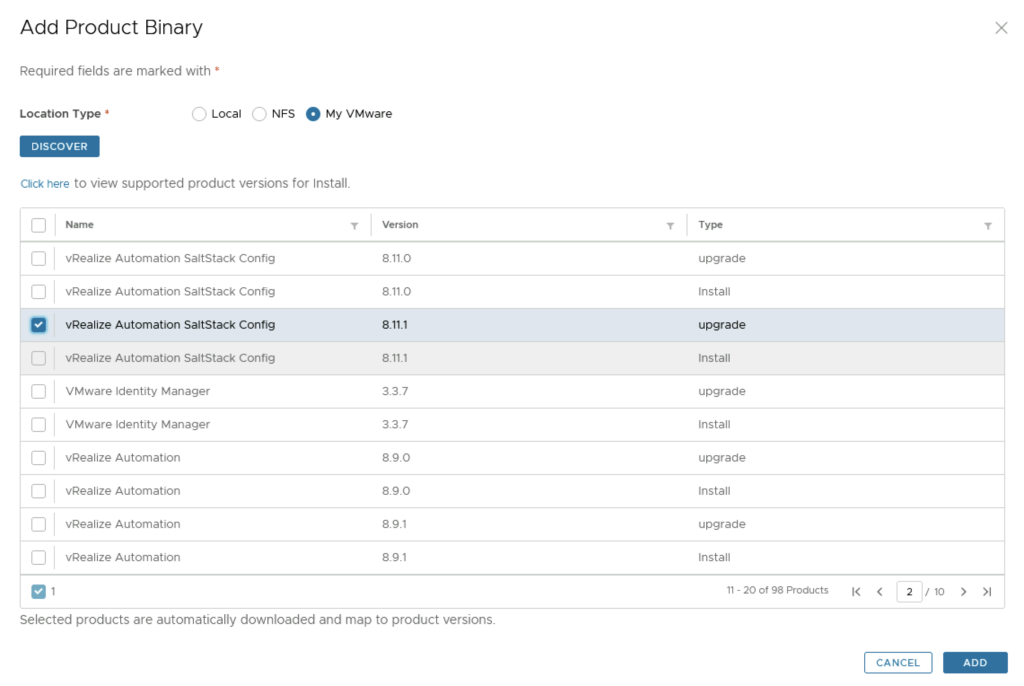
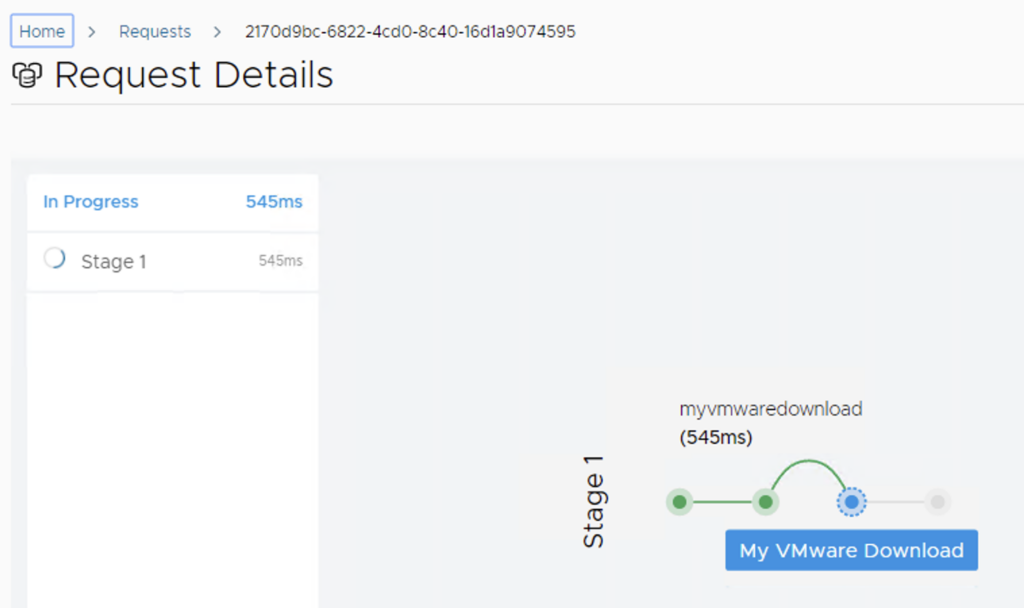
This will create a request and start downloading the package. To view the progress we can click on the Click Here hyperlink

Click on the in Progress button to view the details
We now have to wait for the download to complete
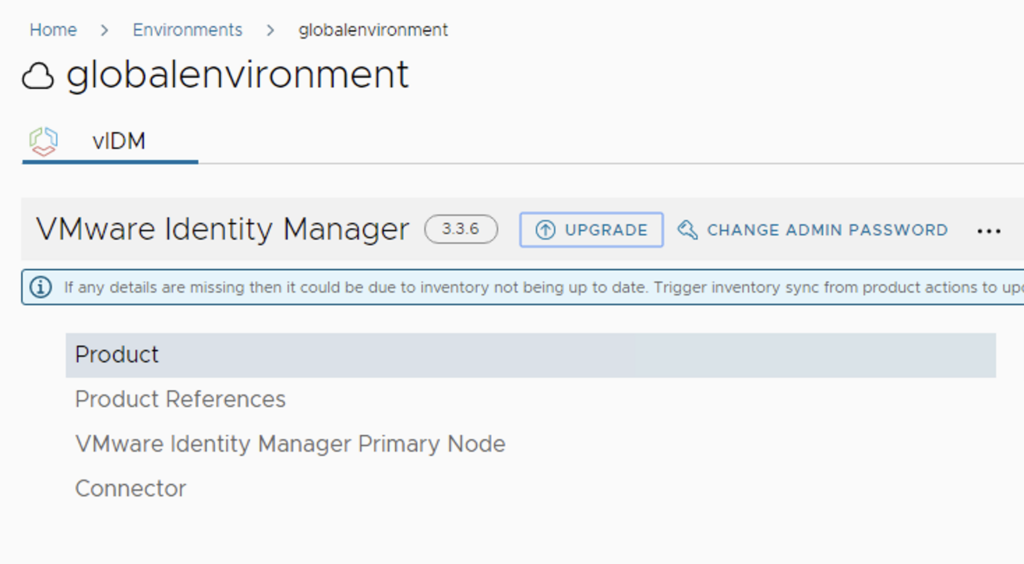
After the download is complete we can go to Environments -> View Details on the environment that includes SSC

Click on Upgrade
An Inventory sync is recommended if the environment has changed since LCM performed the last sync. We trigger the sync from the UI or click on Proceed to continue

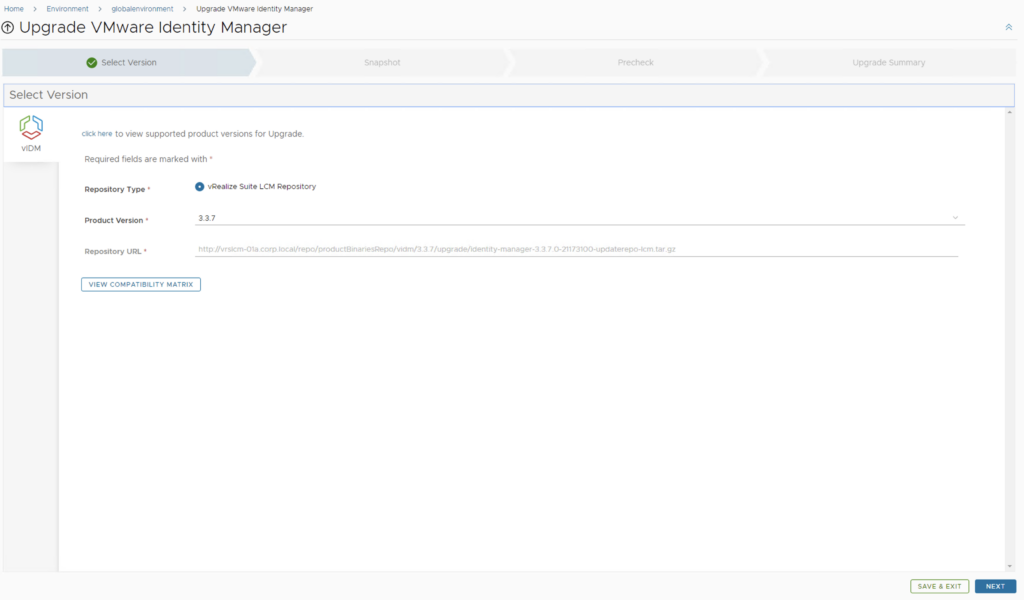
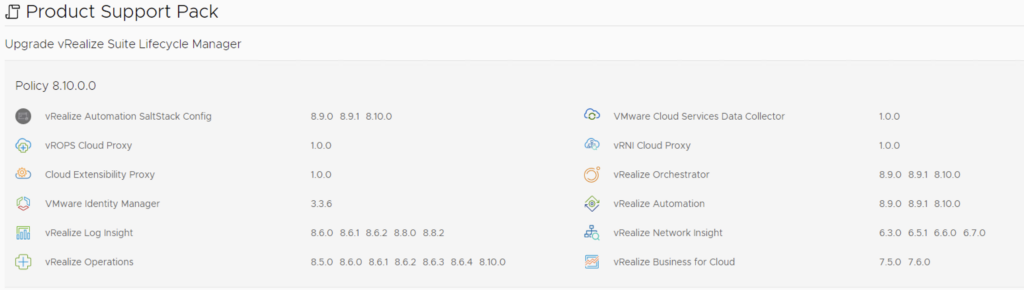
Select product Version 8.11.1 and click Next. We can also review the compatibility matrix to make sure the environment is compatible.
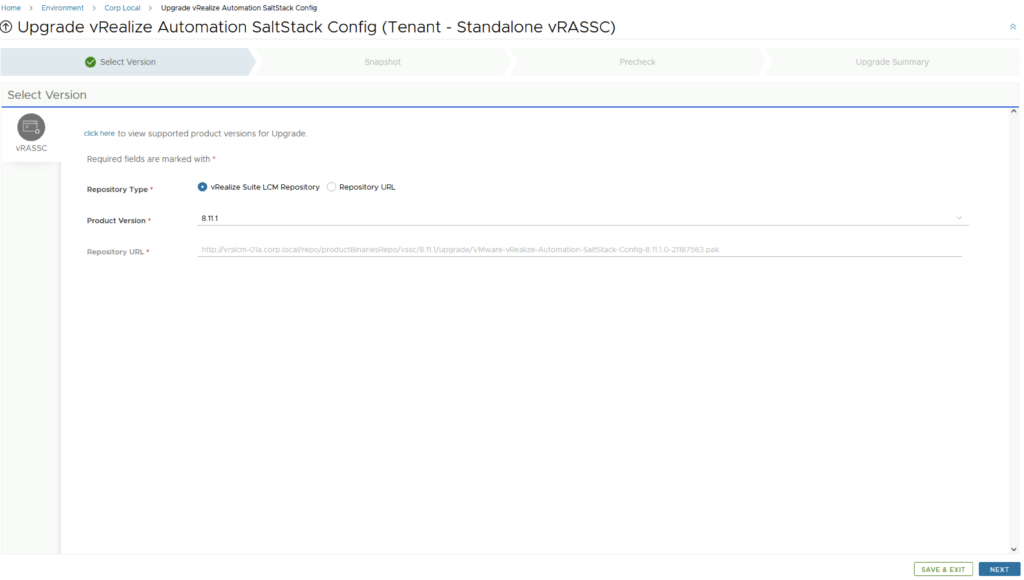
We can automatically create and delete a snapshot part of the upgrade process

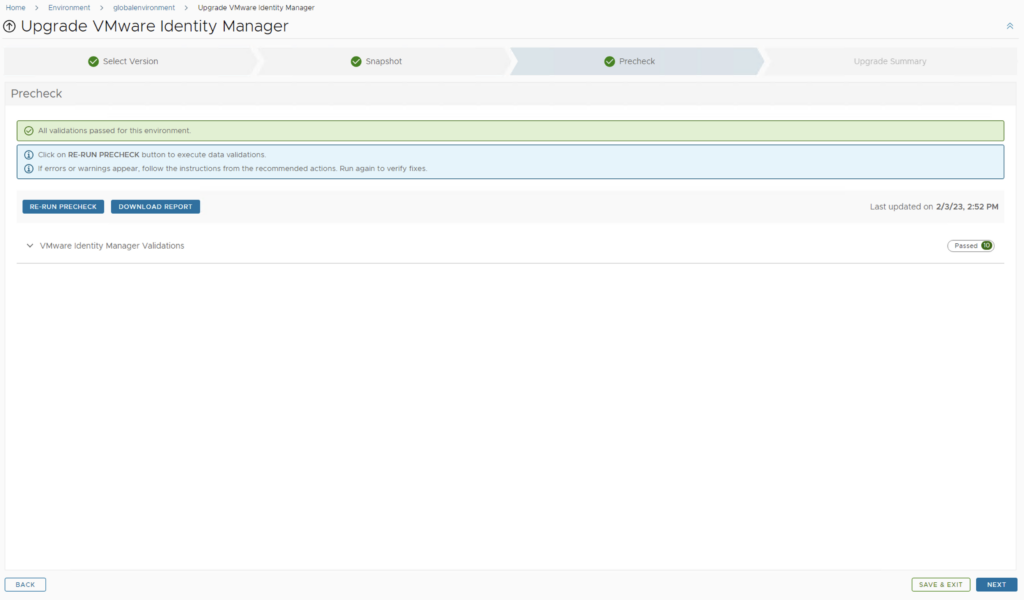
Run the Precheck to make sure there are no errors

Once the check is complete, click on Next. Review the upgrade details and click on Next. We are taken to the progress screen where we can follow the progress.
The system will get rebooted and once its back up we will be on 8.11
Here are a few additional blogs that might be useful post upgrade:
SSC 8.8 sseapi_rpc_queue: could not connect to SSE server
SSC 8.8 urllib3 (1.25.11) or chardet (4.0.0) doesn’t match a supported version